- Introduction to Urban Gardening
- The Basics of Urban Gardening
- Choosing the Right Plants for Urban Gardening
- Tools and Equipment for Urban Gardening
- How to Start Your Own Urban Garden
- Challenges in Urban Gardening and How to Overcome Them
- Success Stories of Urban Gardening
- The Future of Urban Gardening
Introduction to Urban Gardening

Urban gardening, also known as urban horticulture or urban agriculture, encapsulates several methods of growing and cultivating plants in an urban environment. The trend towards urban gardening is rapidly growing as more city dwellers are recognizing the myriad of benefits it offers. In essence, urban gardening is revolutionizing the concept of traditional gardening in cities.
The practice of urban gardening is not just about growing food, but it's also an innovative solution to improve urban biodiversity, reduce environmental pollution, and create sustainable cities. According to a study published in the journal Environmental Research Letters, urban gardens could produce as much as 180 million pounds of food per year in the United States alone.
Urban gardening is a powerful tool that not only enhances food security but also improves the quality of city living, transforming concrete landscapes into green, productive, and sustainable spaces.
Importance of Urban Gardening
- Sustainability:
- Urban gardening promotes sustainability by reducing waste and encouraging recycling. It reduces the carbon footprint by limiting the transportation of goods from rural to urban areas.
- Food Security:
- It increases food security by providing fresh, nutritious, and locally grown produce to urban dwellers.
- Community Building:
- Urban gardens foster community interaction, providing a platform for people to connect and collaborate.
- Education:
- They serve as educational platforms for children and adults alike to learn more about nature, nutrition, and the importance of sustainability.
The trend of urban gardening is not just a fad, it's a necessary shift towards more sustainable lifestyles. The United Nations predicts that by 2050, nearly 70% of the world's population will live in urban areas. This makes urban gardening a pivotal tool in ensuring food security and sustainability in our rapidly urbanizing world.
The Basics of Urban Gardening

For beginners embarking on their urban gardening journey, there are several key factors to consider. These include the available space, access to sunlight, soil quality, and water source. Understanding these basics can help transform a small urban space into a lush, productive garden.
Available Space: The first step in urban gardening is understanding the space available. This could range from a small balcony to a rooftop or even a shared community garden. Regardless of the space, effective planning can maximize its usage. Vertical gardening, for instance, is a popular technique for space optimization in urban gardening.
Sunlight: Sunlight is essential for plant growth. Most edible plants require a minimum of 6-8 hours of sunlight daily. Therefore, it's crucial to assess the sunlight exposure of your space before choosing the plants.
Soil Quality: Good quality soil is pivotal for successful gardening. Urban soil often lacks nutrients and may contain pollutants. It's advisable to use organic compost to enhance soil fertility and ensure healthy plant growth.
Water Source: Consistent watering is key for plant growth. Hence, easy access to a water source is a must. Drip irrigation or self-watering containers can be useful for efficient water management in an urban garden.
Different Types of Urban Gardening
- Balcony Gardening: This is perfect for individuals living in apartments. It involves growing plants in pots or containers on balconies. Herbs, vegetables, and flowering plants can be grown successfully in balcony gardens.
- Rooftop Gardening: This is a great option for individuals with access to a flat roof. Rooftop gardens can significantly reduce heat absorption, contributing to a decrease in the urban heat island effect.
- Community Gardening: This refers to shared spaces where community members can grow their own plants. It's a great option for individuals lacking personal space and promotes community interaction.
Urban gardening, while challenging, can be incredibly rewarding. With careful planning and the right resources, anyone can create their own urban oasis.
Choosing the Right Plants for Urban Gardening

Selecting the right plants is one of the most crucial aspects of urban gardening. The choice of plants largely depends on the local climate, available space and sunlight, and maintenance requirements.
Local Climate: The local climate plays a significant role in plant selection. Certain plants thrive in specific climate conditions. For instance, succulents and cacti do well in warmer climates, while ferns and mosses prefer cooler, shadier environments.
Plant Size: The size of the plant should be proportionate to the available space. For limited spaces, small plants or dwarf varieties are ideal. For larger spaces like rooftops or community gardens, you can opt for larger plants and even small trees.
Maintenance Requirements: Some plants require more care and attention than others. For beginners, low-maintenance plants like herbs, leafy greens, or succulents are recommended. As you gain more confidence and experience, you can explore more complex varieties.
Importance of Seasonal Planting
Seasonal planting is another vital aspect of urban gardening. It refers to planting different varieties of plants during specific seasons when they naturally grow best. This practice maximizes plant productivity and ensures a continuous supply of produce throughout the year. For instance, leafy greens like spinach and lettuce thrive in cool weather, while tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers prefer warm summer months.
Seasonal planting also encourages biodiversity in your garden, attracting a variety of insects and birds, which further contributes to a healthy ecosystem.
By carefully considering these factors, urban gardeners can create a thriving, vibrant garden no matter the size of their space.
Tools and Equipment for Urban Gardening
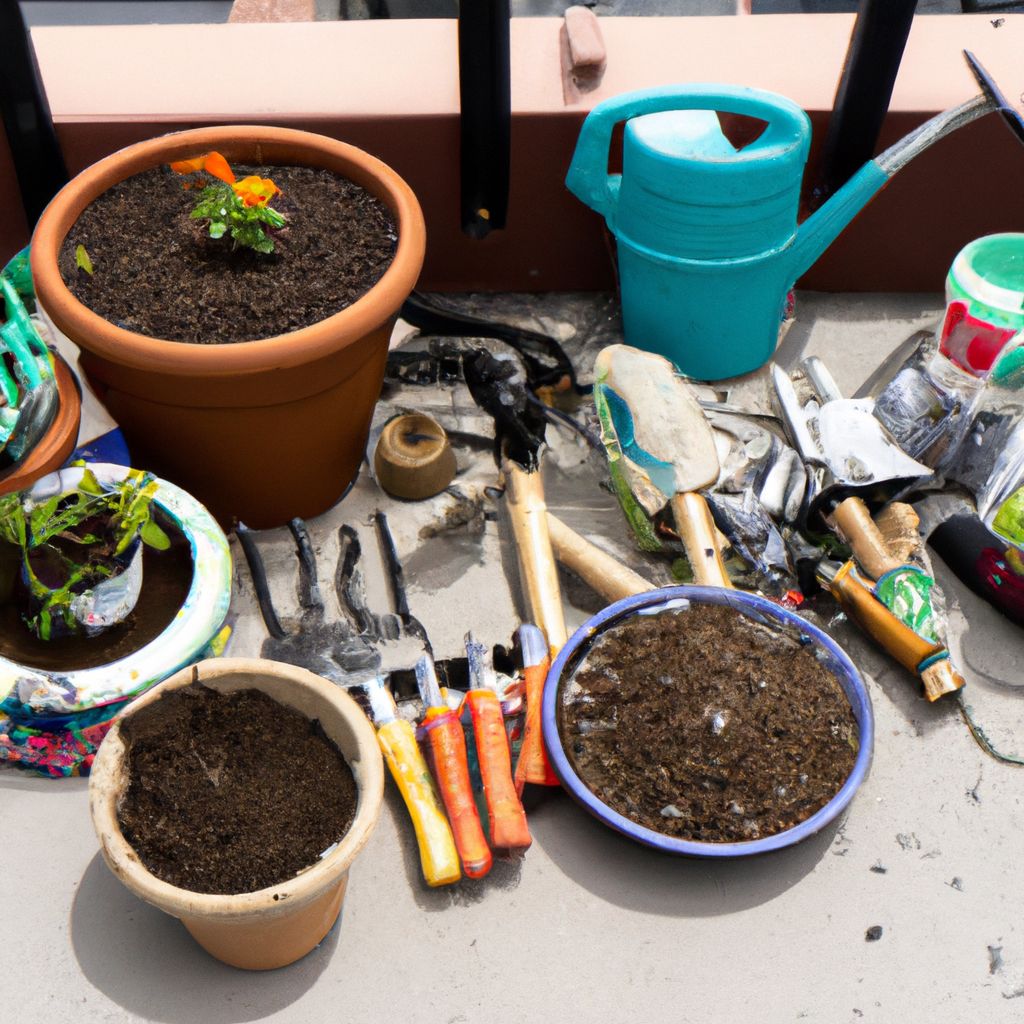

Just like any other form of gardening, urban gardening requires certain tools and equipment to ensure successful plant growth. Here is a list of essential items that every urban gardener needs:
- Pots and Containers:
- As space is often a limiting factor in urban gardening, pots and containers become crucial. They are available in various sizes and materials like plastic, clay, and even recycled materials. Ensure they have adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging.
- Gardening Tools:
- Basic gardening tools include a trowel for digging, a pruning shear for trimming plants, a watering can or hose, and gloves for protection. A soil testing kit can also be beneficial to check soil pH and nutrient levels.
- Soil:
- Good quality potting soil is essential for container gardening. It's light, well-draining, and often enriched with compost or other organic matter.
- Fertilizers:
- Urban plants often need additional nutrients to thrive. Organic fertilizers like compost or worm castings are great options. They not only provide nutrients but also improve soil structure and promote beneficial microbial activity.
- Pest Control:
- Urban gardens are not immune to pests. Natural pest control methods like neem oil, insecticidal soap, or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can be effective.
While these are the basic tools and equipment needed for urban gardening, the specific requirements may differ based on the type of plants you choose to grow and the space available. Regardless, with the right tools in hand, urban gardening can be a gratifying endeavor.
How to Start Your Own Urban Garden
Starting an urban garden might seem daunting, but with a systematic approach, it can be a smooth and rewarding journey. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Planning the Garden
Firstly, assess the space available to you. It could be a balcony, a rooftop, or a community garden. Take note of the amount of sunlight it receives and its proximity to a water source. Draw a rough sketch of the space and plan where you would like to place your pots or containers.
Step 2: Preparing the Space
Clean the area and ensure it's ready for planting. If you're using pots, make sure they have sufficient drainage holes. If you're planning a rooftop garden, check with a professional to ensure the roof can handle the weight.
Step 3: Choosing the Plants
Choose plants based on the local climate and the amount of sunlight your space receives. For beginners, low-maintenance plants like herbs or leafy greens are a good starting point. Also, consider the size of the plants to ensure they don't overcrowd your space.
Step 4: Planting
Fill your pots or containers with good quality potting soil, leaving some space at the top. Dig a hole about twice the size of your plant's root ball, place the plant in, and cover with soil. Water thoroughly after planting.
Step 5: Maintenance
Regular watering is crucial, but be careful not to overwater. Monitor your plants for any signs of pests or diseases. Use organic fertilizers to provide additional nutrients and promote healthy growth.
Starting an urban garden may require some effort and patience, but the benefits it offers are manifold. From serving as a source of fresh produce to providing a green oasis in the concrete jungle, an urban garden is indeed a worthwhile venture.
Challenges in Urban Gardening and How to Overcome Them
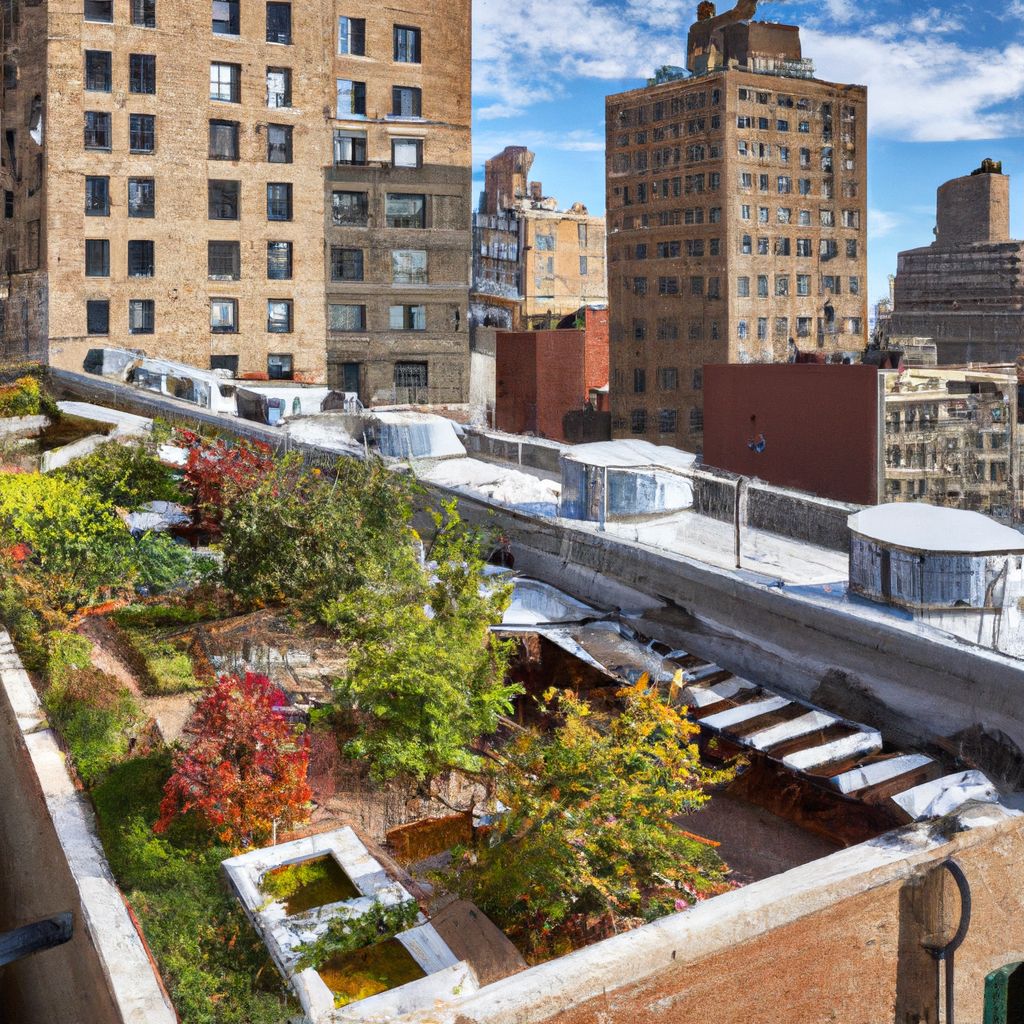

While urban gardening offers numerous benefits, it also brings its own set of challenges. However, with careful planning and ingenious solutions, these obstacles can be effectively overcome.
Limited Space: In urban settings, space constraints are a common issue. However, this can be addressed through effective space utilization techniques. Vertical gardening, using hanging pots, trellises, and tiered planters, can significantly increase your growing space. Also, opting for dwarf or miniature varieties of plants can ensure they don't outgrow their containers.
Insufficient Sunlight: Buildings and other structures can often block sunlight, making it difficult for sun-loving plants to thrive. To overcome this, choose shade-tolerant plants like ferns, hostas, or certain herbs like mint and parsley. Alternatively, reflective surfaces can be used to increase the amount of light available to plants.
Water Issues: Urban gardeners often face challenges related to water availability and drainage. For effective water management, consider using self-watering pots or install a drip irrigation system. Ensure all containers have proper drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other diseases.
Poor Soil Quality: Urban soil is often depleted of nutrients and may contain contaminants. To address this, use good quality potting mix and enrich it regularly with organic matter like compost or worm castings.
Despite these challenges, urban gardening is a fulfilling pursuit, transforming concrete city spaces into green, productive, and sustainable environments. With the right resources and techniques, anyone can cultivate a thriving urban garden.
Success Stories of Urban Gardening
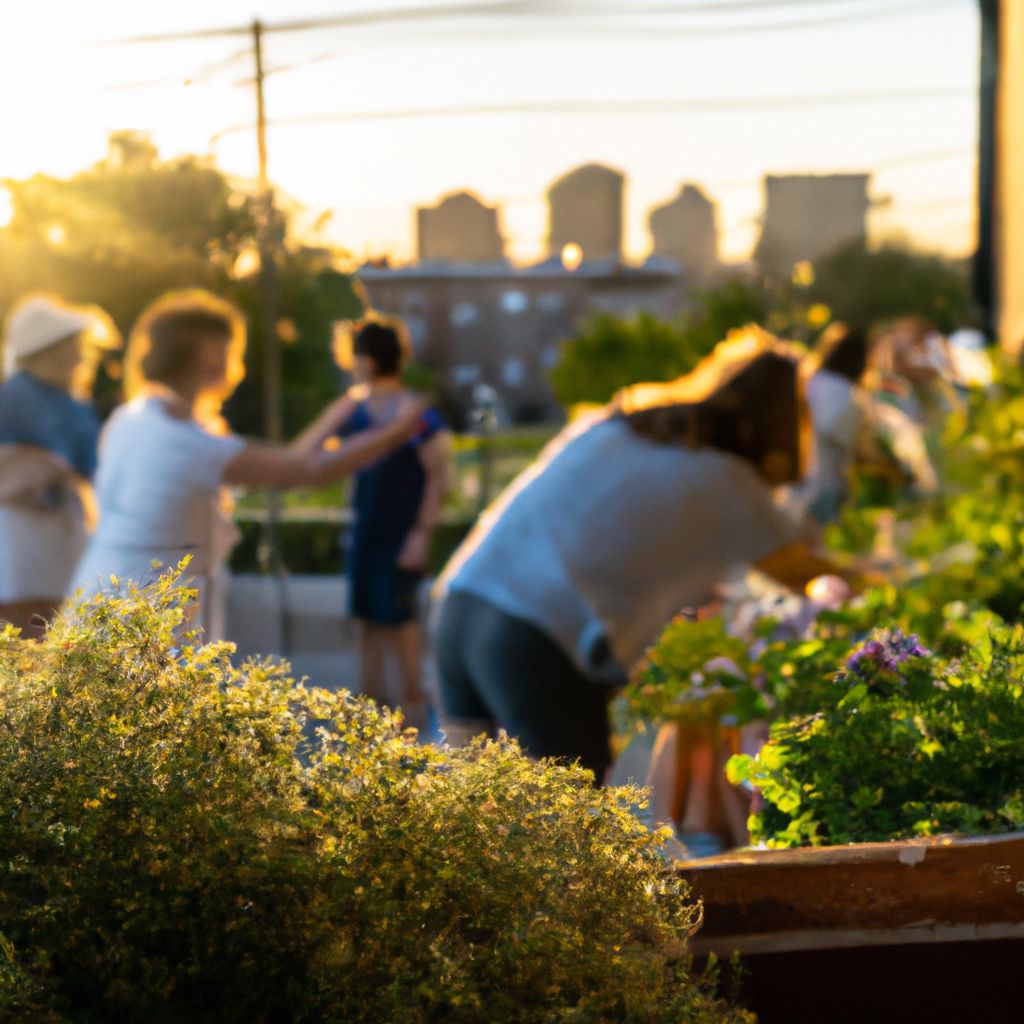

Across the globe, urban gardening is being embraced as a viable solution to food security, sustainability, and community building. Here are a few inspiring success stories:
The Edible Schoolyard Project: Founded by renowned chef Alice Waters, this initiative transformed an asphalt lot at a public middle school in Berkeley, California, into a thriving organic garden. The garden not only provides produce for the school's lunch program but also serves as an outdoor classroom where students learn about nutrition, food systems, and the environment.
The Fenway Victory Gardens: Located in Boston, these gardens date back to World War II and are the oldest continuously operating Victory Gardens in the United States. Over 500 plots are maintained by local residents, yielding fresh produce, flowers, and herbs. The site serves as a testament to the resilience and sustainability of urban gardening.
Rooftop Republic: This social enterprise is revolutionizing the urban landscape of densely populated Hong Kong by transforming underutilized rooftops into vibrant urban farms. They not only grow organic produce but also conduct workshops and events to promote urban farming and sustainable living.
GreenThumb Community Gardens: In New York City, the GreenThumb program supports over 550 community gardens, making it the largest community gardening program in the nation. These gardens provide fresh produce, green spaces, and community engagement in neighborhoods across the city.
These success stories highlight the potential of urban gardening to transform city landscapes, enhance food security, and foster community spirit, inspiring many more to embark on their own urban gardening journey.
The Future of Urban Gardening
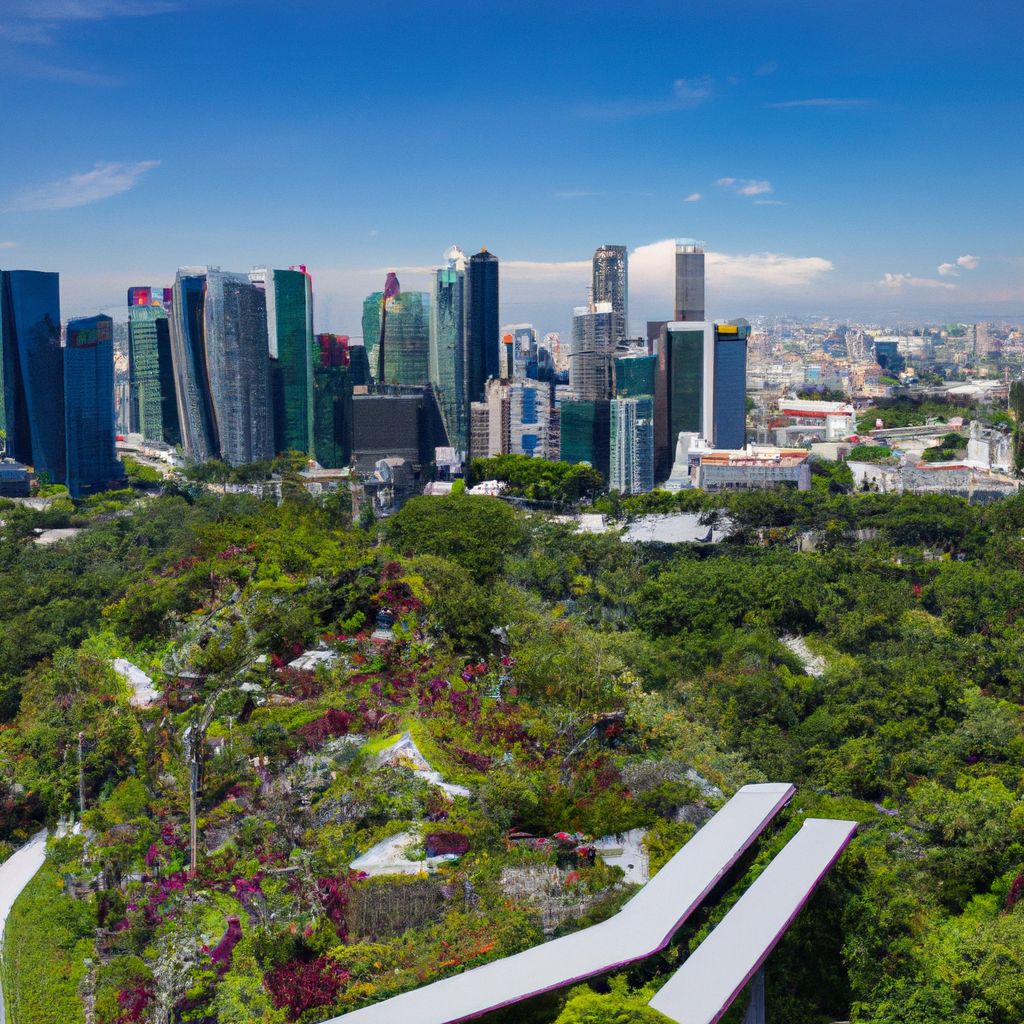

Urban gardening is more than just a trend - it's an essential part of the future of sustainable living. With the world's urban population projected to increase significantly in the coming decades, urban gardening is set to play a critical role in food production, environmental conservation, and community building.
Urban gardens have the potential to significantly contribute to food security. They provide fresh, locally grown produce, reducing dependence on long-distance food transportation and the carbon footprint associated with it. In the future, we can expect urban gardens to play a vital role in feeding the burgeoning urban population.
From an environmental perspective, urban gardens contribute to biodiversity, help reduce the urban heat island effect, and improve air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. As cities continue to expand, incorporating green spaces in the form of urban gardens will be essential for environmental conservation and creating livable urban habitats.
Urban gardening also promotes community engagement and social well-being. Community gardens provide a platform for people to connect, collaborate, and learn from each other. They can serve as hubs for environmental education, promoting awareness about sustainable practices among urban dwellers.
With advancements in technology, the future of urban gardening also holds exciting possibilities. Innovations like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics can maximize yield in small spaces, making urban gardening more efficient and sustainable.
In conclusion, the future of urban gardening looks promising. It holds the potential to transform city landscapes, improve food security, and foster sustainable communities, making it an integral part of sustainable urban development.