- Understanding Mountaineering
- Importance of Safety in Mountaineering
- Pre-Mountaineering Health Check
- Essential Safety Gear for Mountaineering
- Safety Measures while Climbing
- Emergency Situations and First Aid
- Importance of Training and Preparation
- Conclusion: Cultivating a Safety Mindset
Understanding Mountaineering

Mountaineering, also known as mountain climbing, is a sport that involves ascending mountains. It is a physically demanding activity that tests one's endurance, agility, and strength. Mountaineering is not just about reaching a peak; it's about the journey, the adventure, the exploration, and the self-discovery.
There are three main types of mountaineering:
- : This type involves climbing up rock formations, often with the help of ropes and other equipment.
- : This type involves ascending ice formations such as icefalls, frozen waterfalls, and cliffs and rock slabs covered with ice refrozen from flows of water.
- : Also known as high-altitude mountaineering, this type involves climbing mountains in high altitudes, often in conditions of snow, ice, and rock.
Mountaineering provides numerous health benefits. It improves cardiovascular fitness, flexibility, muscle strength, and mental health. A study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that activities such as mountain climbing can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and improve longevity. Furthermore, the solitude and tranquility of the mountains can have a positive impact on mental health, reducing stress and promoting a sense of well-being.
However, mountaineering also poses significant risks, including altitude sickness, hypothermia, and injuries from falls. Therefore, it's vital to understand the basics of mountaineering and the necessary safety measures. Learning the correct techniques, using appropriate equipment, and understanding the terrain and weather conditions can significantly reduce these risks.
Mountaineering safety measures aren't just about preventing accidents. They're about ensuring climbers can respond effectively when things go wrong. This could mean knowing how to administer first aid, navigate in adverse weather, or make the right decisions when fatigued. Safety measures are an integral part of mountaineering that cannot be overlooked.
Importance of Safety in Mountaineering

Safety in mountaineering is paramount. Given the inherent risks and extreme conditions involved in this sport, the importance of safety measures cannot be overstated.
Mountaineering involves various risks, including:
- : This can occur when you ascend too quickly and your body doesn't have enough time to adapt to the decreased air pressure and oxygen level.
- : These can lead to hypothermia and frostbite, both potentially life-threatening conditions.
- : Falls from height can result in severe injuries or death.
- : These can bury climbers under tons of snow, leading to suffocation or trauma.
However, most of these risks can be mitigated with proper safety measures. For instance, the risk of altitude sickness can be reduced by proper acclimatization, hydration, and, if necessary, medication. Appropriate clothing and equipment can protect against extreme weather conditions, while sound climbing techniques and safety equipment can prevent falls. Knowledge of the terrain and weather conditions can help avoid the risk of avalanches.
Failure to adhere to safety measures can have severe consequences. According to the American Alpine Club, there were 151 mountaineering fatalities in North America between 2010 and 2016, many of which could have been prevented with appropriate safety measures. In addition to the risk of death or injury, failure to follow safety measures can lead to long-term health issues and psychological trauma.
Therefore, it's essential to understand and adhere to safety measures in mountaineering. This not only ensures your safety but also enhances your mountaineering experience, allowing you to enjoy the sport while respecting nature and its challenges.
Pre-Mountaineering Health Check
A thorough health check is a crucial step before embarking on any mountaineering expedition. Mountaineering demands a high level of physical and mental fitness, and pre-existing health conditions can escalate into severe issues at high altitudes.
Physical health: Mountaineering requires cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and endurance. A pre-mountaineering health check should assess these aspects of fitness and screen for any underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes, that could worsen with the physical stress of mountaineering.
Mental health: Mountaineering also demands mental resilience. The isolation, harsh conditions, and physical challenges can be psychologically demanding. Therefore, a mental health check, including screening for conditions such as anxiety and depression, is equally important.
Common health issues that can occur while mountaineering include:
- : Symptoms include nausea, headache, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Proper acclimatization and hydration can help prevent altitude sickness.
- : This can occur in extreme cold conditions. Wearing appropriate clothing and having adequate food and drink can help prevent hypothermia.
- : This occurs when skin and underlying tissues freeze. Wearing appropriate gloves, socks, and boots can prevent frostbite.
- : This can result from inadequate fluid intake or excessive sweating. Regularly drinking water can prevent dehydration.
Preparation is key to preventing these issues. This includes physical training, mental conditioning, and learning about high-altitude physiology and mountain medicine. It's also crucial to have a plan in place for dealing with any health issues that may arise during the expedition.
Remember, mountaineering is not about pushing your limits at the expense of your health. It's about enjoying the journey while maintaining your health and safety.
Essential Safety Gear for Mountaineering

Proper safety gear is fundamental to the safety and success of a mountaineering expedition. Here are some essential items:
- Climbing Helmet
- This protects your head from falling debris and impacts. Look for a helmet that fits well, is comfortable, and meets the safety standards set by organizations like the Union Internationale des Associations d'Alpinisme (UIAA). You can purchase climbing helmets at outdoor sports stores or online.
- Mountaineering Boots
- These provide grip, support, and insulation. Boots should be waterproof, well-insulated, and comfortable. It's important to try on boots before purchasing to ensure a good fit. They can be bought from outdoor sports stores or online.
- Crampons
- Crampons are spiked devices attached to boots to provide traction on ice and snow. They should be sturdy and compatible with your boots. Crampons can be purchased from outdoor gear shops or online.
- Ice Axe
- An ice axe is used for balance, arresting falls, and cutting steps in ice. It should be lightweight and the right length for your height. Ice axes can be found in outdoor gear stores or online.
- Carabiners and Quickdraws
- These are used for securing ropes and gear. They should be lightweight, strong, and easy to use with gloves on. Carabiners and quickdraws can be purchased from outdoor gear shops or online.
- Ropes
- Mountaineering ropes should be lightweight, durable, and designed for the type of climbing you'll be doing. They can be purchased from outdoor gear shops or online.
- First Aid Kit
- A comprehensive first-aid kit is essential for dealing with injuries. It should include bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, and medication for altitude sickness. It can be purchased from any pharmacy or online.
When buying mountaineering gear, it's important to consider the quality, durability, and functionality of the items. It's also recommended to seek advice from experienced mountaineers or professional guides.
Safety Measures while Climbing
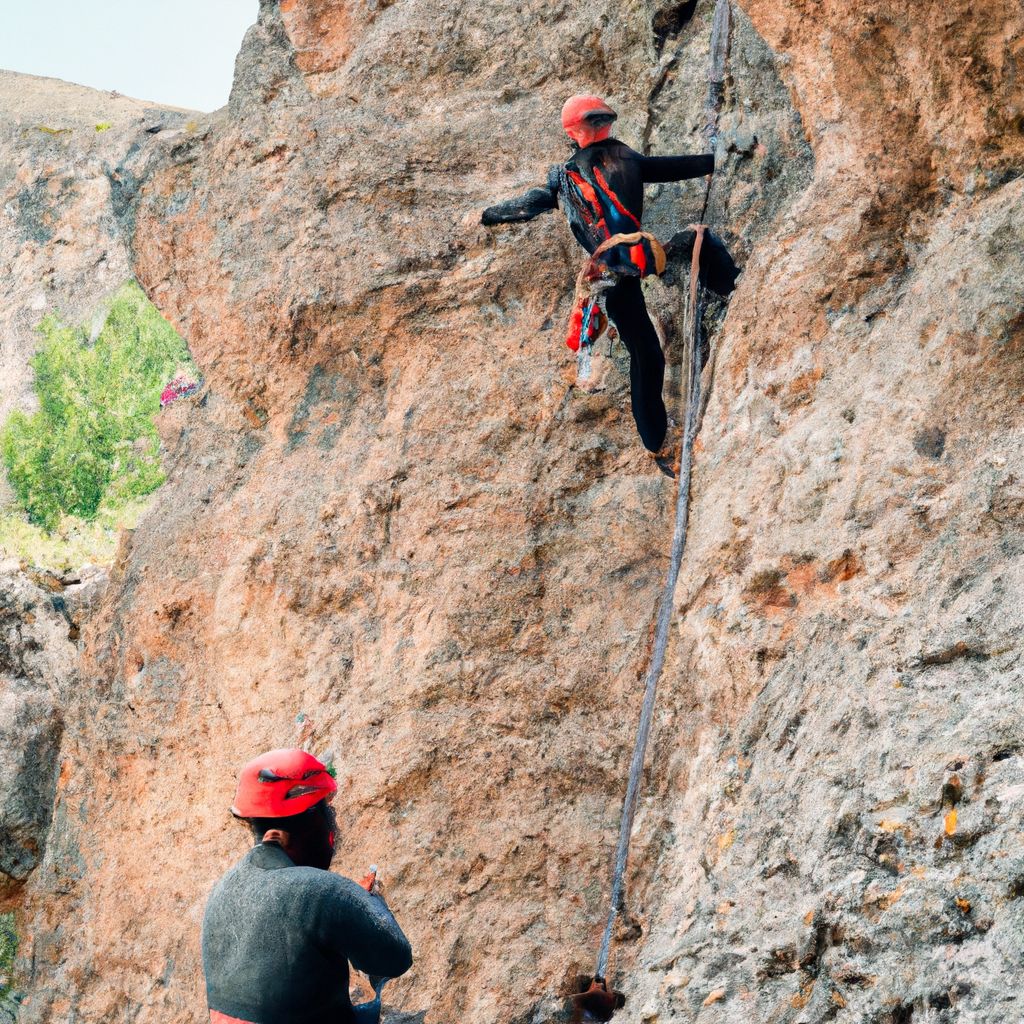

Climbing a mountain is a significant undertaking that requires careful preparation and adherence to safety measures. Here are some of the key safety measures to consider while climbing:
- Proper Use of Gear
- Ensure you know how to use your gear correctly. This includes knowing how to fit your helmet and harness, attach crampons, use your ice axe, and tie knots. Improper use of gear can lead to accidents.
- Monitor Weather Conditions
- Mountains have their own microclimates, and conditions can change rapidly. It's crucial to check the weather forecast before you set off and monitor conditions as you climb. If the weather turns bad, be prepared to turn back.
- Maintain Communication
- Keep in touch with your team and make sure everyone is accounted for at all times. Use walkie-talkies or mobile phones to maintain communication. It's also important to inform someone not on the expedition about your plans and expected return time.
- Stay Hydrated and Nourished
- High-altitude climbing can lead to dehydration and loss of appetite. Drink plenty of water and eat high-energy foods to maintain your strength and energy levels.
- Respect the Mountain
- Follow the principles of Leave No Trace. This includes disposing of waste properly, not removing or disturbing natural features, and minimizing campfire impacts.
- First Aid Knowledge
- Everyone in the team should have basic first aid knowledge. This includes knowing how to treat wounds, fractures, hypothermia, and altitude sickness.
Remember, safety should always be your primary concern when climbing. No summit is worth risking your life for. If conditions become dangerous, don't hesitate to turn back. There's always another day to climb.
Emergency Situations and First Aid
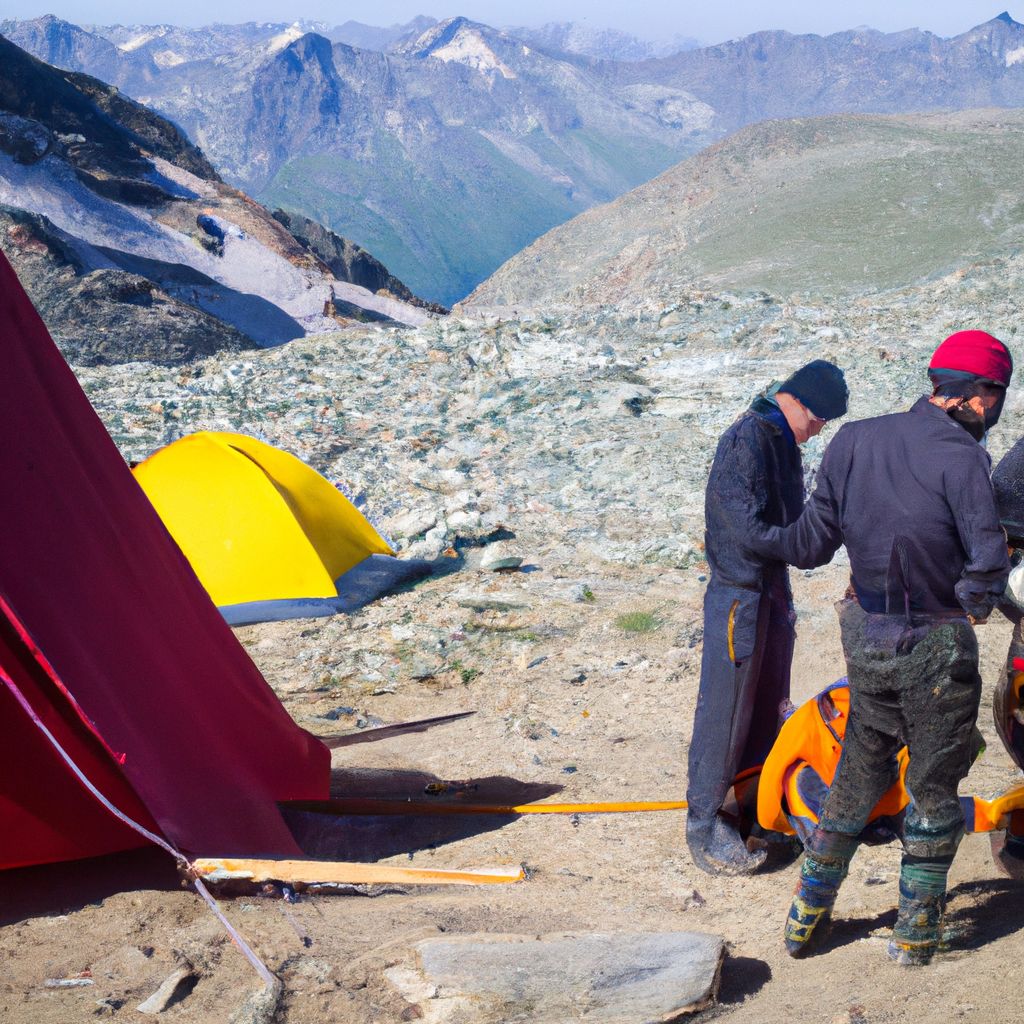

Despite careful planning and preparation, emergencies can occur during mountaineering expeditions. These can range from minor injuries to life-threatening situations. Knowing how to handle these emergencies is crucial.
Potential emergencies include:
- : Falls can lead to fractures, head injuries, sprains, and more.
- : This can cause headaches, nausea, dizziness, and in severe cases, high altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) or high altitude cerebral edema (HACE).
- : This can occur when body temperature drops below normal, leading to shivering, confusion, and loss of coordination.
- : This is the freezing of body tissues, usually the fingers, toes, nose, and ears.
- : This can result from inadequate fluid intake or excessive sweating.
Knowing first aid can mean the difference between life and death in these situations. It allows you to provide immediate care to an injured or ill person, which can prevent the condition from worsening and promote recovery.
Here are some basic first aid tips for common mountaineering injuries and illnesses:
- Falls
- For fractures, immobilize the affected area using a splint. For sprains, use the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation.
- Altitude sickness
- Descend to a lower altitude as soon as possible. Rest and hydrate. Medications like Diamox can help with symptoms.
- Hypothermia
- Move the person to a sheltered location. Remove wet clothing and wrap the person in warm blankets. Give warm drinks, if possible.
- Frostbite
- Never rub the frostbitten area. Warm it gently by soaking in warm (not hot) water.
- Dehydration
- Prevent dehydration by drinking plenty of water, even if you're not thirsty. If dehydration occurs, rehydrate slowly and steadily.
It's recommended to take a wilderness first aid course before embarking on a mountaineering expedition. This will equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to handle medical emergencies in the mountains.
Importance of Training and Preparation
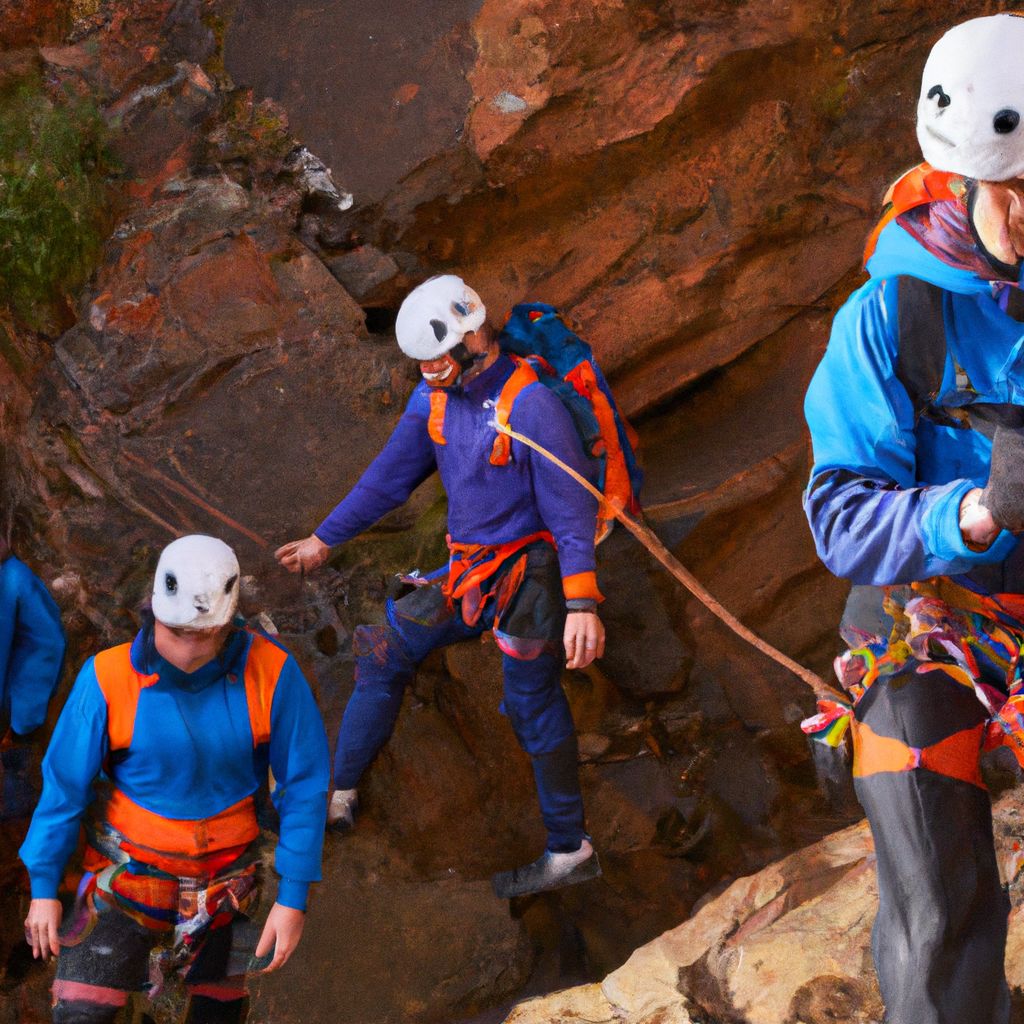

Proper training and preparation are critical for a successful and safe mountaineering expedition. They increase your physical and mental readiness, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance your overall mountaineering experience.
Training for mountaineering typically involves the following components:
- Cardiovascular Training
- This improves your body's ability to use oxygen, which is vital when climbing at high altitudes where oxygen levels are lower. Activities can include running, cycling, and swimming.
- Strength Training
- This builds the strength needed to carry heavy packs and climb steep slopes. Exercises should target the core and lower body muscles. They can include squats, lunges, and planks.
- Endurance Training
- This prepares your body for the prolonged physical effort required in mountaineering. Long-distance hiking with a weighted backpack is a good way to build endurance.
- Technical Training
- This involves learning the specific skills required for mountaineering, such as using climbing gear, navigating, and providing first aid.
Proper training can help prevent common mountaineering injuries, improve performance, and increase your enjoyment of the sport. It can also help prepare you mentally for the challenges of mountaineering, building resilience and confidence.
When choosing a training program, it's important to find one that matches your fitness level, mountaineering goals, and available time for training. Many outdoor sports centers and mountaineering clubs offer training programs. You can also find online training plans designed specifically for mountaineering.
Remember, preparation is the key to success in mountaineering. As the old saying goes, "The more you sweat in training, the less you bleed in combat."
Conclusion: Cultivating a Safety Mindset
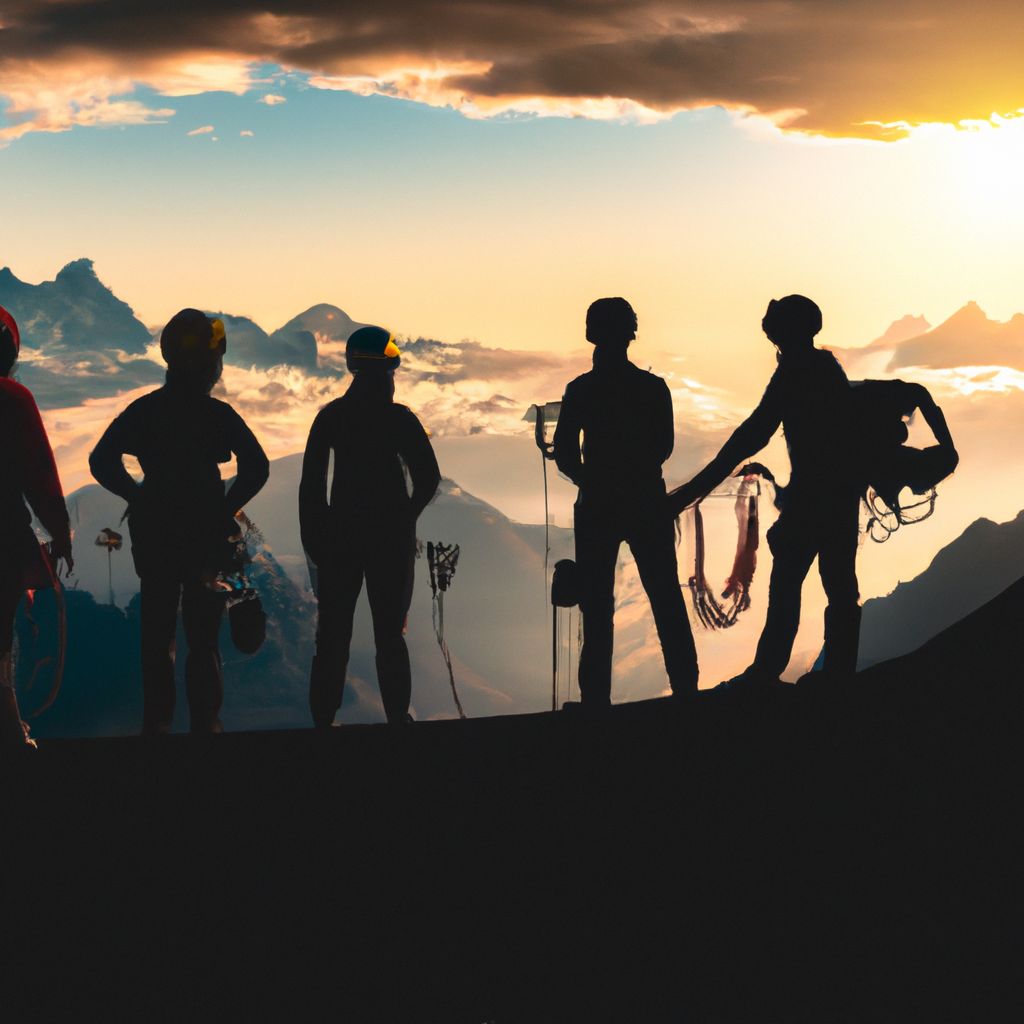

In conclusion, safety must be at the forefront of your mind when embarking on a mountaineering expedition. It's not just about having the right gear or the physical strength to climb; it's about cultivating a safety mindset. This involves understanding the risks, preparing thoroughly, adhering to safety measures, and making prudent decisions on the mountain.
Remember, mountaineering is not a race or a test of endurance. It's an adventure, a journey of self-discovery, and a chance to connect with nature. By prioritizing safety, you not only protect yourself and others, but you also enhance your enjoyment of this amazing sport.
So, take the time to prepare, train, and learn. Respect the mountain and its challenges. And above all, stay safe. The mountain will always be there, and so should you.








